 Deep Shadows
Deep Shadows Deep Shadows
Deep ShadowsOverview Deep Shadow Benefits
Deep Shadow Cons Deep Shadows Vs. Ray Tracing |
Deep Shadows were developed during |
|
|
|
|
The Deep Shadow Controls Shadow Type Pixel Samples Motion Blur Volume Interpretation
|
|
|
|
|
| Creating Deep Shadows For information about creating deep shadows refer to: Deep Shadows- Colored Shadows. |
|
Deep Shadow Examples |
|
 |
 |
|
Fog with Deep Shadows |
Fog with Traditional Shadow Map |
 |
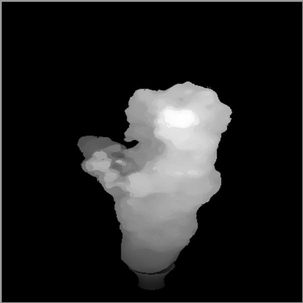 |
|
A Deep Shadow Map |
A Traditional Shadow Map |
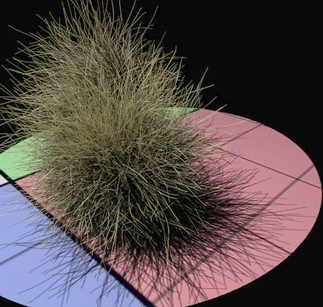 |
 |
|
Fur with Deep Shadows |
Fur with Traditional Shadows |
 |
|
| Motion Blurred Shadows With Deep Shadows, motion blurred objects can now cast shadows with motion blur. The Motion Blur parameter must be enabled to cause the calculation of this additional motion blurred data. This parameter should only be enabled when motion blurred shadows are required, for efficiency. Increasing the Pixel Samples improves the quality of the blurred shadow (and increases render times). |
Colored Shadows Semi-transparent objects can cast colored shadows. Note that the opacity of the surface shader is stored in the deep shadow, not the surface color. That's right, it's the opacity color and not the surface color. Actually it's the inverse color of the opacity. You might find Slim's Invert Color node useful for this. (It allows the hue to be inverted independent of the value.) For an example see: Deep Shadows: Colored Shadows |
|
|
|
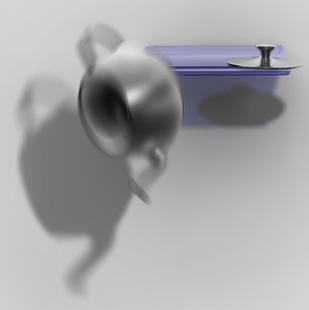
| Other Possibilities: Fake
Caustics
Deep Shadows can be used to create different types of effects. One of these possibilities is fake caustics. In the image on the right the caustic effect was created using Deep Shadow maps, no ray tracing or photon maps was required. An example file is provided: Deep Shadows: Fake Caustics |
|
|
Pixar Animation Studios
|